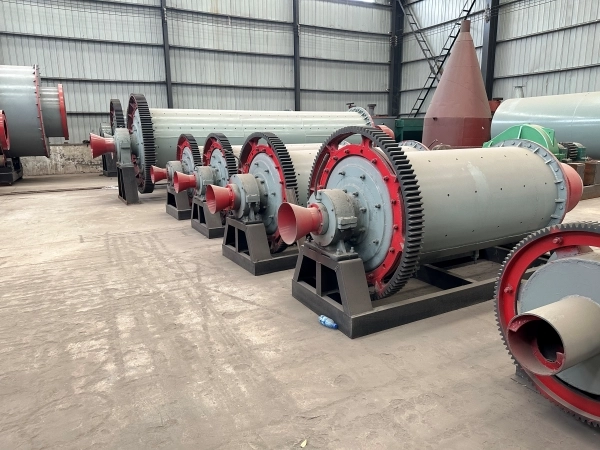
A ball mill is a crucial piece of equipment used for grinding and blending materials, commonly utilized in mineral processing, ceramics, and pyrotechnics industries. Understanding the principles of operation and best practices for efficient and safe operation is essential for achieving optimal performance and minimizing downtime. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive guide on how to operate a ball mill effectively.
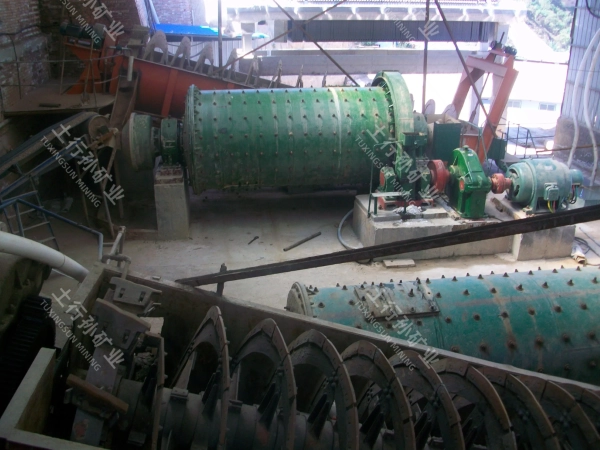

01. Basic Components and Structure
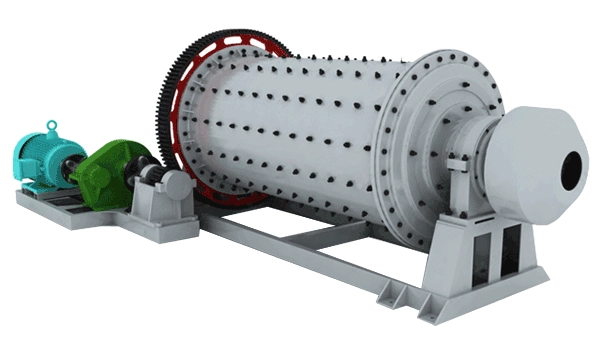
The basic components and structure of a ball mill play a crucial role in its operation and performance. Understanding these elements is essential for effectively operating the equipment.
1. Cylindrical Shell
The ball mill consists of a cylindrical shell that houses the grinding media and the material being processed. The shell is typically made of steel or rubber and is lined with replaceable liners to protect it from wear and tear caused by the grinding media and the processed material.
2. Grinding Media
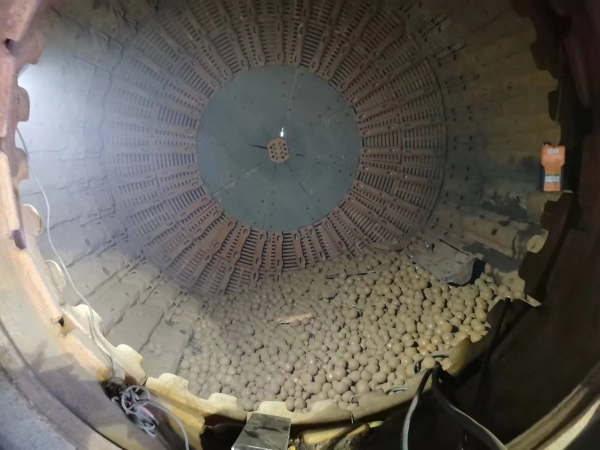
The grinding media used in a ball mill are typically steel or ceramic balls. They are responsible for pulverizing the material by applying impact and friction forces. The size and type of grinding media used depend on the material being processed and the desired fineness of the final product.
3. Drive System
The drive system of a ball mill includes the motor, gearbox, and couplings. The motor provides the rotational power to the mill, while the gearbox ensures the desired speed and torque are transmitted to the mill's rotating drum. Couplings connect the motor and the gearbox to facilitate smooth power transmission.
4. Rotating Drum
The rotating drum, also known as the mill drum or shell, is where the grinding media and material are placed. It rotates on its axis, causing the grinding media to cascade and create impacts that break down the material into smaller particles.
5. Feed and Discharge Mechanisms
The feed mechanism introduces the material into the mill, while the discharge mechanism allows the ground material to exit the mill. The feed mechanism may include a hopper, conveyor belt, or chute, depending on the specific application. The discharge mechanism can be either through a grate with openings to control the size of the discharged particles or through an overflow system.
6. Liners
The inner surface of the cylindrical shell is lined with replaceable liners to protect it from abrasion and impact caused by the grinding media. The liners are typically made of rubber, metal, or composite materials. They also help in lifting the grinding media to a certain height, promoting cascading and efficient grinding.
7. Control System
Many modern ball mills are equipped with a control system that regulates various parameters such as mill speed, material feed rate, and temperature. The control system ensures optimal operation, improves efficiency, and allows for remote monitoring and adjustments.

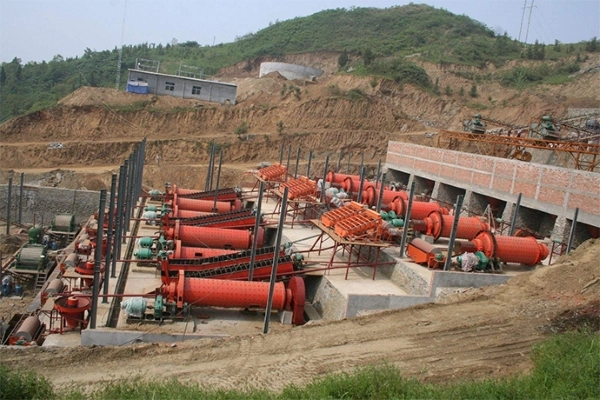
(1830 Overflow Ball Mill)
02. Pre-Operation Procedures
Before starting the ball mill, certain pre-operation procedures should be followed to ensure a safe and efficient operation. These include inspecting the mill for any defects, ensuring all the components are in good condition, and verifying that the lubrication system is well-greased. Additionally, it is important to check the grinding media for proper size and weight.
1. Mill Inspection
Before starting the ball mill, conduct a thorough inspection of the equipment. Look for any visible signs of damage, such as cracks, leaks, or misalignment. Check the structural integrity of the mill, including the foundation, trunnion bearings, and gears. Inspect the electrical connections and ensure they are secure. If any defects or issues are detected, they should be addressed and resolved before proceeding.
2. Component Check
Verify that all components of the ball mill are in good condition. This includes checking the integrity of the grinding media and ensuring they are of the correct size and weight. Inspect the liners for wear and tear, and replace them if necessary. Examine the drive system, including the motor, gearbox, and couplings, and ensure they are functioning properly. If any components are damaged or worn out, they should be repaired or replaced before starting the mill.
3. Lubrication
Proper lubrication is crucial for the smooth operation of a ball mill. Check the lubrication system and ensure it is well-greased. This includes lubricating the trunnion bearings, gear ring, and pinion gear. Use the recommended lubricants and follow the manufacturer's instructions. Insufficient lubrication can lead to increased friction, excessive wear, and premature failure of components.
4. Safety Measures
Before starting the mill, ensure that all safety measures are in place. This includes wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as safety glasses, gloves, and earplugs. Make sure the safety guard is in position and functioning correctly. Familiarize yourself with the emergency shutdown procedure and have it readily accessible.
5. Communication
Establish clear communication channels with other personnel involved in the operation. Ensure that everyone understands their roles and responsibilities. It is essential to have effective communication to coordinate activities, address any concerns, and respond promptly to any emergencies.

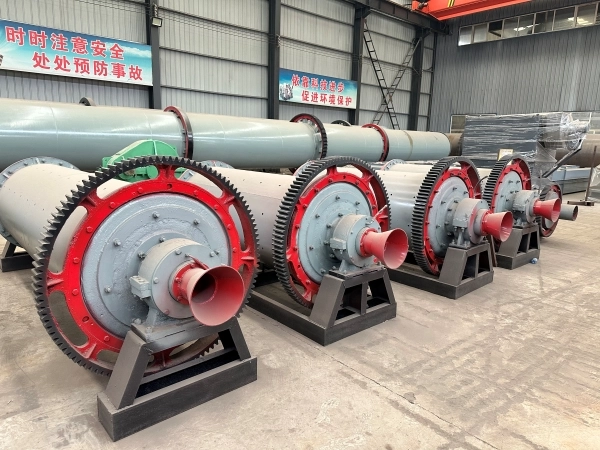
(Ball Mill)
03. Starting the Ball Mill
To start the ball mill, follow these steps:
1. Close the safety guard and ensure the drum is correctly seated on the coupling.
2. Place the drum on a level surface and add the pre-determined amount of grinding media.
3. Ensure that the rotation direction of the mill is correct by checking the arrow on the mill's housing.
4. Turn on the motor and observe the rotation of the mill. If everything appears normal, proceed to the next step.
04. Operation
During operation, several factors should be monitored and controlled to ensure optimal performance. These include:
1. Mill Speed
Adjust the mill speed to achieve the desired grinding results. Higher speeds result in finer particles, while lower speeds provide coarser particles. However, the speed should not exceed the critical speed, which can cause the grinding media to centrifuge instead of cascading.
2. Material Feed Rate
Control the feed rate to maintain a consistent material flow into the mill. Overfeeding can lead to excessive wear and inefficient grinding, while underfeeding may cause the mill to run empty, leading to damage.
3. Residence Time
The residence time of the material in the mill affects the grinding efficiency. It is important to ensure an adequate residence time to achieve the desired fineness.
4. Grinding Media Size and Distribution
Regularly monitor and adjust the grinding media size and distribution to optimize the grinding process. This can be done by adding or removing grinding media or adjusting their size.
5. Milling Temperature
Monitor the temperature inside the mill to prevent overheating, which can affect the quality of the ground material. Cooling systems, such as water jackets or air fans, can be employed to maintain an appropriate temperature.
6. Discharge and Classification
Ensure that the ground material is discharged properly from the mill. Fine particles may require a classifier system to separate them from coarser particles.

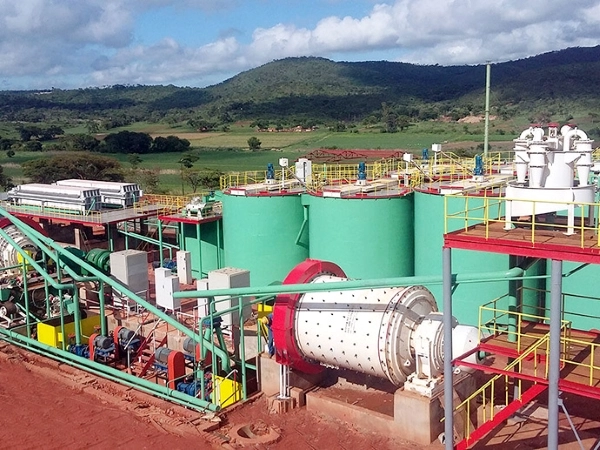
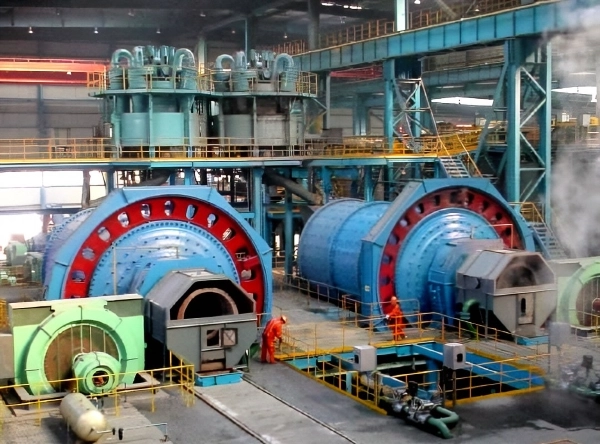
(Ball Mill in A Gold Plant)
05. Safety Considerations
Operating a ball mill comes with inherent risks, and it is crucial to prioritize safety. Some safety considerations include:
1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Always wear the appropriate PPE when working with a ball mill. This may include safety glasses, gloves, hearing protection, and safety shoes. PPE helps protect you from potential hazards such as flying debris, spills, and noise.
2. Equipment Inspection
Before starting the ball mill, thoroughly inspect the equipment for any signs of damage, wear, or malfunction. Check the electrical connections, lubrication system, safety guards, and emergency shut-off mechanisms. Address any issues or defects before proceeding.
3. Lockout/Tagout Procedures
Follow lockout/tagout procedures to ensure that the ball mill is de-energized and isolated before performing any maintenance or repair tasks. This involves disconnecting the power source, locking out electrical switches, and clearly tagging the equipment to prevent accidental energization.
4. Safety Guards
Ensure that all safety guards are in place and functioning correctly. Safety guards help prevent access to moving parts, protect against flying debris, and contain the grinding media within the mill. Never operate the mill without the appropriate safety guards in place.
5. Emergency Shutdown
Familiarize yourself with the emergency shutdown procedures for the ball mill. Clearly understand how to quickly and safely shut down the equipment in case of an emergency, such as equipment malfunction, excessive vibration, or personnel injury. Communicate the shutdown procedures to all personnel involved.
6. Material Handling
Take precautions when handling materials for the ball mill. Use proper lifting techniques, such as using lifting equipment or assistance when handling heavy loads. Be aware of potential hazards associated with the material being processed, such as toxicity, flammability, or explosiveness.
7. Fire Safety
Keep fire safety in mind when operating a ball mill. Ensure that the work area is clear of flammable materials. Have appropriate fire extinguishers readily available and know how to use them. Regularly inspect and maintain the mill's electrical components to minimize the risk of electrical fires.
8. Training and Communication
Provide adequate training to all personnel involved in the operation of the ball mill. Ensure that they are familiar with the equipment, safety procedures, and emergency protocols. Encourage open communication and reporting of any safety concerns or incidents.
9. Regular Maintenance
Perform regular maintenance on the ball mill to keep it in good working condition. This includes lubrication, inspection of critical components, and replacement of worn-out parts. Proper maintenance reduces the risk of equipment failures and enhances overall safety.
10. Risk Assessment
Conduct a thorough risk assessment of the ball mill operation to identify and mitigate potential hazards. Assess the risks associated with electrical systems, rotating parts, material handling, and any other specific hazards related to your specific application.
06Conclusion
Operating a ball mill requires a deep understanding of its components, principles, and operational procedures. By following the guidelines provided in this comprehensive guide, operators can optimize the performance of the ball mill, achieve efficient grinding, and maintain a safe working environment. Regular monitoring, maintenance, and adherence to safety protocols are essential for prolonging the equipment's lifespan and preventing accidents. Stay vigilant and prioritize safety at all times to ensure successful ball mill operation.
- Random article
- Popular articles
- Popular comments
- Magnetic separation and beneficiation process for bauxite
- Tin ore gravity separation+flotation+gravity separation process
- Gravity beneficiation process for iron ore
- Cyanide Gold Preparation
- Branch serial flow flotation process for lead-zinc ore
- Lithium Ore Processing: Gravity Separation and Flotation
- Uranium Ore Radioactive Treatment Process














Leave a message with your needs or comments
Add comment: