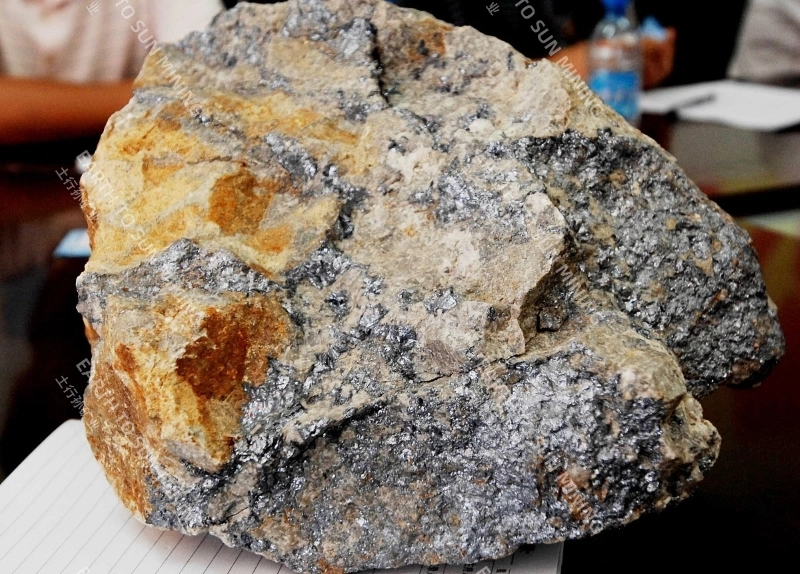

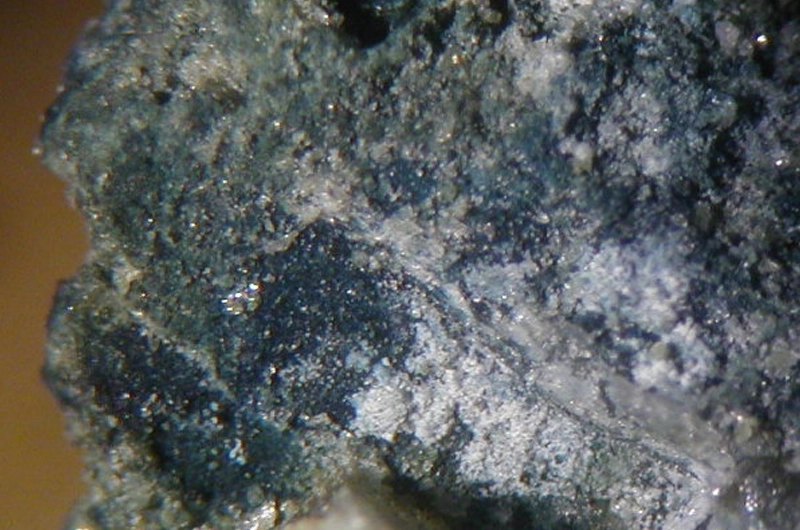
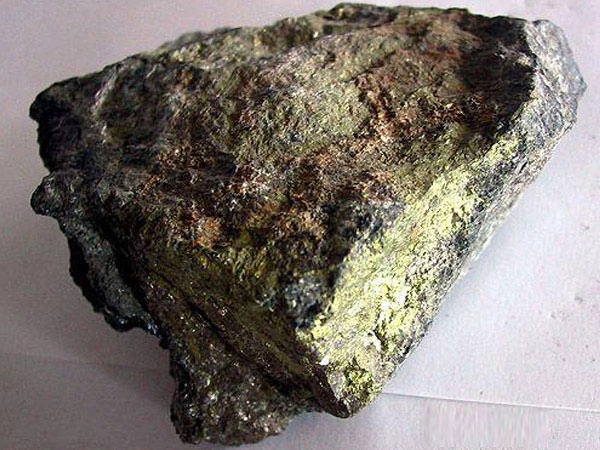
Molybdenum is rarely distributed and relatively concentrated in nature. Currently, there are more than 20 known molybdenum minerals, including molybdenite, molybdenite, molybdenite, and calcium molybdate. These four types of molybdenum minerals are currently of industrial value; Molybdenite accounts for more than 98% of the world’s mining output, and the other three are secondary oxidation minerals of molybdenite. Molybdenum ore beneficiation should prevent over grinding, and the process generally adopts a multi-stage grinding and selection process. The conventional process is: rough grinding produces coarse concentrate, sweeping tailings to recover other metals, and the coarse concentrate is further ground in 2-3 stages and selected multiple times to obtain molybdenum concentrate.
Polymetallic ores containing magnetic minerals are selected separately or in combination with various metal minerals through a combined process of magnetic separation and flotation. Suitable for minerals with high magnetic iron content.
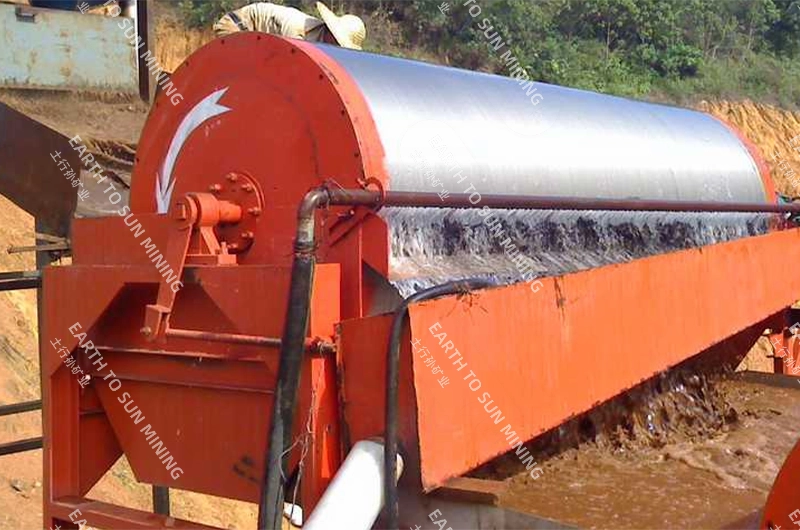

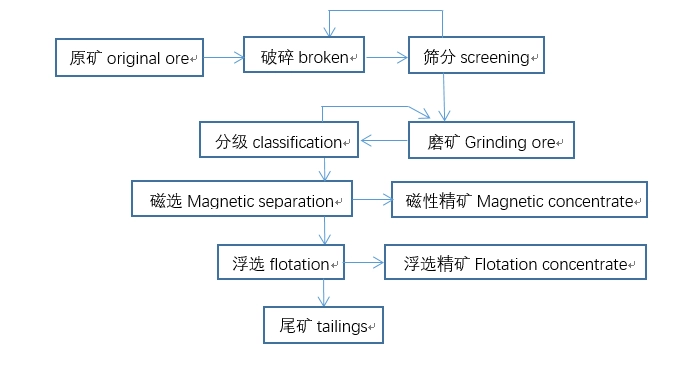
Typical beneficiation plant
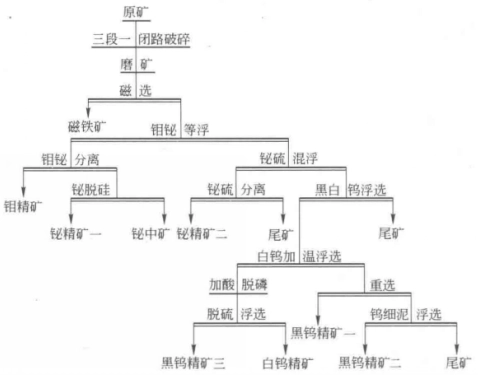
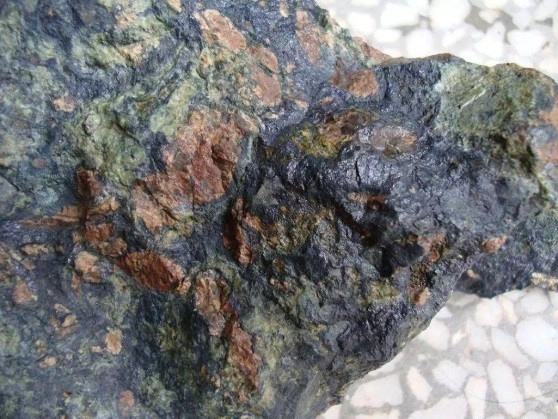
The Shizhuyuan tungsten bismuth molybdenum fluorite polymetallic beneficiation plant mainly consists of molybdenite and molybdenite minerals, while other metal minerals include tungsten minerals, bismuth minerals, cassiterite, pyrite, etc. Gangue minerals mainly include garnet, fluorite, calcite, quartz, etc. The principle process is as follows:
- Random article
- Popular articles
- Popular comments
- Carbon leaching beneficiation process for gold mines
- Sand gold beneficiation process
- Zirconium Ore Separation: Gravity and Magnetic Methods
- chrome ore processing:Advanced Magnetic Separation Processing Technology
- Chromium Ore Gravity Separation and Flotation Process
- Efficient purification of manganese ore by magnetic separation process
- Essential Guide to Tantalum-Niobium Ore Flotation Process







Leave a message with your needs or comments
Add comment: