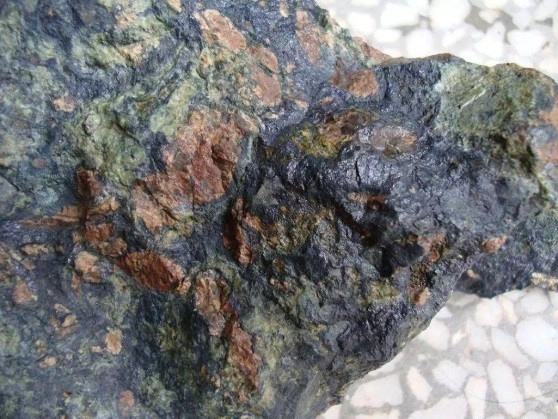

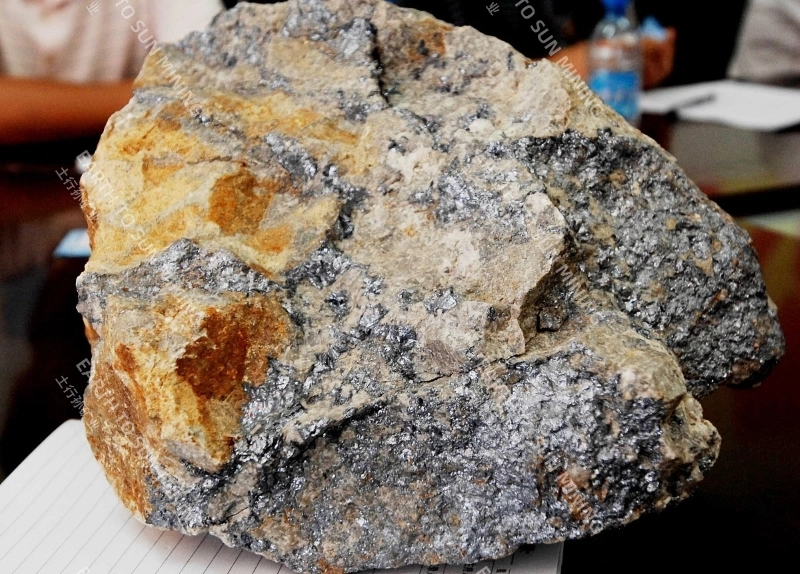
Molybdenum is rarely distributed and relatively concentrated in nature. Currently, there are more than 20 known molybdenum minerals, including molybdenite, molybdenite, molybdenite, and calcium molybdate. These four types of molybdenum minerals are currently of industrial value; Molybdenite accounts for more than 98% of the world’s mining output, and the other three are secondary oxidation minerals of molybdenite. Molybdenum ore beneficiation should prevent over grinding, and the process generally adopts a multi-stage grinding and selection process. The conventional process is: rough grinding produces coarse concentrate, sweeping tailings to recover other metals, and the coarse concentrate is further ground in 2-3 stages and selected multiple times to obtain molybdenum concentrate.
After crushing and grinding, the raw ore is roughly ground to produce rough concentrate. The rough concentrate is further ground in 2-3 stages and selected multiple times to obtain molybdenum concentrate.

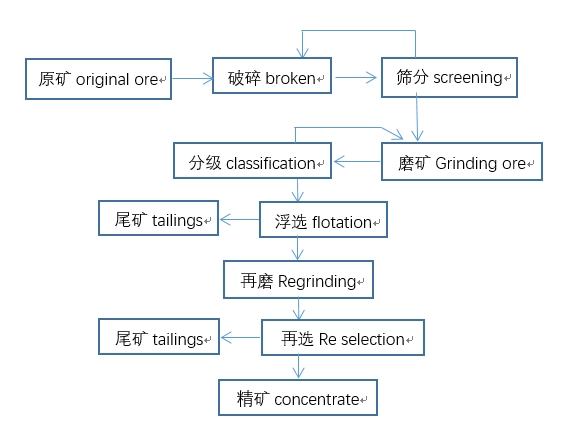
Typical beneficiation plant
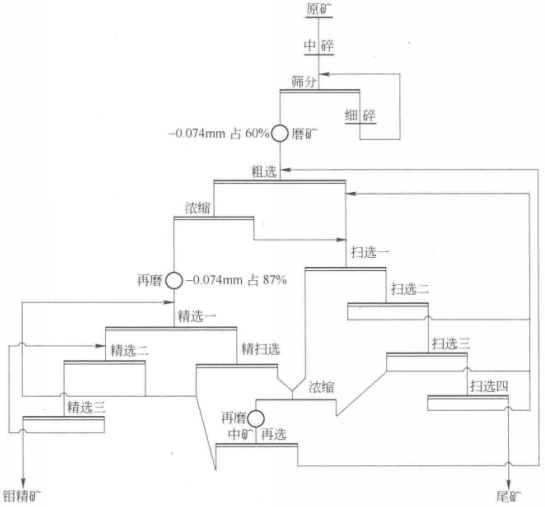
The ore dressing plant of Luoyang Luanchuan Molybdenum Industry Second Company mainly contains metal minerals such as pyrite, molybdenite, and magnetite, while vein minerals mainly include garnet, diopside, quartz, plagioclase, etc. The specific beneficiation process is as follows:
- Random article
- Popular articles
- Popular comments
- Magnetic separation and beneficiation process for bauxite
- Iron ore reverse flotation process
- Gold Mine Combined Beneficiation Process
- Lithium ore positive flotation process
- Zirconium Ore Separation: Gravity and Magnetic Methods
- Complete Manganese Ore Gravity Separation Process
- Tantalum-Niobium Ore Processing: Gravity, Magnetic, and Electric Separation







Leave a message with your needs or comments
Add comment: